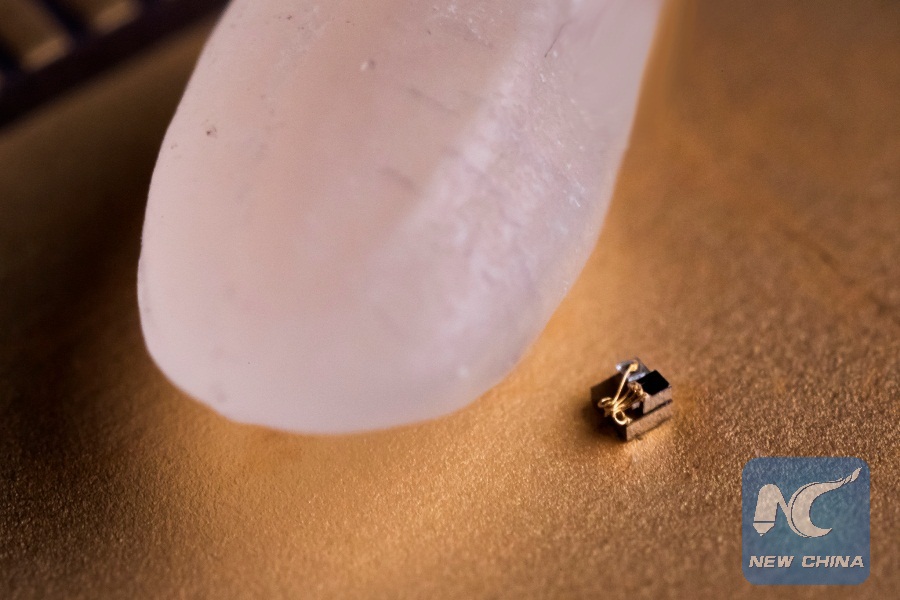
Grain of rice next to tiny computer (Credite: the University of Michigan)
CHICAGO, June 22 (Xinhua) -- Researchers at the University of Michigan (UM) in the United States has come out with the world's smallest "computer," a device that measures just 0.3 mm to a side, completely dwarfed by a grain of rice.
Unlike traditional desktop computers that always have their program and data there no matter unplugged or having power back, these new microdevices lose all prior programming and data as soon as they lose power.
"We are not sure if they should be called computers or not. It's more of a matter of opinion whether they have the minimum functionality required," said David Blaauw, a professor of electrical and computer engineering, who led the development of the new system.
In addition to the RAM and photovoltaics, the new computing devices have processors and wireless transmitters and receivers. As they are too small to have conventional radio antennae, they receive and transmit data with visible light. A base station provides light for power and programming, and it receives the data.
Designed as a precision temperature sensor, the new device converts temperatures into time intervals, defined with electronic pulses. The intervals are measured on-chip against a steady time interval sent by the base station and then converted into a temperature.
As a result, the computer can report temperatures in minuscule regions, such as a cluster of cells, with an error of about 0.1 degrees Celsius.
The system is very flexible and could be reimagined for a variety of purposes. The researchers chose precision temperature measurements because of a need in oncology.
"Since the temperature sensor is small and biocompatible, we can implant it into a mouse and cancer cells grow around it," said Gary Luker, a UM professor of radiology and biomedical engineering.
"We are using this temperature sensor to investigate variations in temperature within a tumor versus normal tissue and if we can use changes in temperature to determine success or failure of therapy."
The researchers also look forward to what purposes others will find for their latest microcomputing device, named the Michigan Micro Mote.
The study was presented on Thursday at the 2018 Symposia on VLSI Technology and Circuits.

